Table of Contents
Identity
We are using Keycloak for our identity management and SSO.
Getting an account
If you are a GlasHack member and would like an account for any of our SSO enabled services please send a request to one of the following Keycloak admins with your preferred username:
- Ava
- Jonas
Once an account has been created, you can go to https://identity.lab.glashack.space:8443/realms/glashack/account/ to sign in and set your password.
This account should then permit allow authentication to any of the services listed below (although some services have extra internal permissions which must be configured before you'll have useful access).
SSO enabled services
Keycloak server setup
VM config
Our Keycloak instance is hosted in a VM with the following specific configuration:
- Based on the debian-13-cloudinit-template
- VMID: 104
- Memory: 2GiB
- Processors: 2 (with type: host to enable required extensions)
- MAC address: BC:24:11:C2:74:DF (used for DHCP reservation .104 to match VMID)
- Hostname: identity
- Cloud-Init used to add initial SSH keys and configure DHCP + DNS (lab.glashack.space, 10.0.100.1)
Docker is installed on the VM using the instructions available at: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/debian/ and https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/
Docker Compose
The following compose file is located under /home/debian/compose.yml to run Keycloak and PostgreSQL
services:
keycloak:
container_name: keycloak_app
image: quay.io/keycloak/keycloak:26.5.2
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "8443:8443"
volumes:
- ./certbot/cert/:/etc/letsencrypt:ro # map certificates to container
environment:
KEYCLOAK_ADMIN: ${KEYCLOAK_USER}
KEYCLOAK_ADMIN_PASSWORD: ${KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD}
KC_HOSTNAME: ${KEYCLOAK_URL}
KC_DB_URL: jdbc:postgresql://keycloak_postgres:5432/keycloak
KC_DB: postgres
KC_DB_USERNAME: ${POSTGRES_USER}
KC_DB_PASSWORD: ${POSTGRES_PASSWORD}
KC_HTTPS_CERTIFICATE_FILE: /etc/letsencrypt/live/identity.lab.glashack.space/fullchain.pem
KC_HTTPS_CERTIFICATE_KEY_FILE: /etc/letsencrypt/live/identity.lab.glashack.space/privkey.pem
depends_on:
- keycloak_postgres
networks:
- keycloak-network
command:
- start
keycloak_postgres:
container_name: keycloak_postgres
image: postgres:18.1
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: keycloak
POSTGRES_USER: ${POSTGRES_USER}
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: ${POSTGRES_PASSWORD}
POSTGRES_PORT: 5432
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql
networks:
- keycloak-network
networks:
keycloak-network:
name: keycloak-network
driver: bridge
volumes:
postgres_data:
A .env file following this template is used to provide the variables:
KEYCLOAK_USER="xxx" KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD="xxx" KEYCLOAK_URL="identity.lab.glashack.space" POSTGRES_USER="xxx" POSTGRES_PASSWORD="xxx"
The KEYCLOAK_USER/PASSWORD options are only used for the initial admin account. Personal admin accounts have since been created in the Keycloak UI and the default one deleted.
HTTPS certificates
Certbot is used to get LetsEncrypt certificates for the Keycloak web interface. https://certbot-dns-rfc2136.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
A key is generated on the DNS server and added into the config.
router# cd /var/named/etc
router# tsig-keygen -a HMAC-SHA512 identity-certbot
key "identity-certbot" {
algorithm hmac-sha512;
secret "<secret key>";
};
router# vim named.conf # add key to DNS config with permission to update lab.glashack.space zone.
This key is then provided to certbot on the identity server using the following file. /home/debian/certbot/credentials.ini
# Target DNS server dns_rfc2136_server = 10.0.100.1 # Target DNS port dns_rfc2136_port = 53 # TSIG key name dns_rfc2136_name = identity-certbot # TSIG key secret dns_rfc2136_secret = "<identity-certbot dns key generated above>" # TSIG key algorithm dns_rfc2136_algorithm = HMAC-SHA512
debian@identity:~/certbot$ mkdir -p cert/work-dir cert/logs-dir debian@identity:~/certbot$ sudo certbot certonly --dns-rfc2136 --dns-rfc2136-credentials ./credentials.ini -d 'identity.lab.glashack.space' -d 'identity.lab.glashack.space' --config-dir cert/ --agree-tos --no-eff-email --work-dir cert/work-dir/ --logs-dir cert/logs-dir/ debian@identity:~/certbot$ sudo chmod -R 775 cert/*/
The last command fixes a permissions issue were the Keycloak server can't read the certs. There may be a better way of doing this…
Keycloak configuration
Realms / administrators
Once Keycloak is up and running a new admin user was created in the Keycloak realm and the default one deleted. The default realm is used for management of the Keycloak server itself. All glashack config is done in a new realm called glashack.
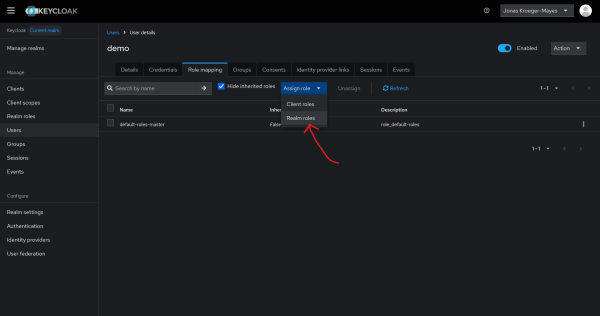
To give a new user admin permissions you must create a user and then under Role mapping assign the required Realm roles.
Clients
vmhost
- Client ID: vmhost
- Name: Glasgow Hackerspace Proxmox
- Root URL: https://vmhost.lab.glashack.space/
- Home URL: https://vmhost.lab.glashack.space/
- Valid redirect URLs: https://vmhost.lab.glashack.space/*
- Web origins: *
- Admin URL: https://vmhost.lab.glashack.space/
- Client authentication: On
- Authorization: On
- Authentication flow: Standard, Implicit, Direct access